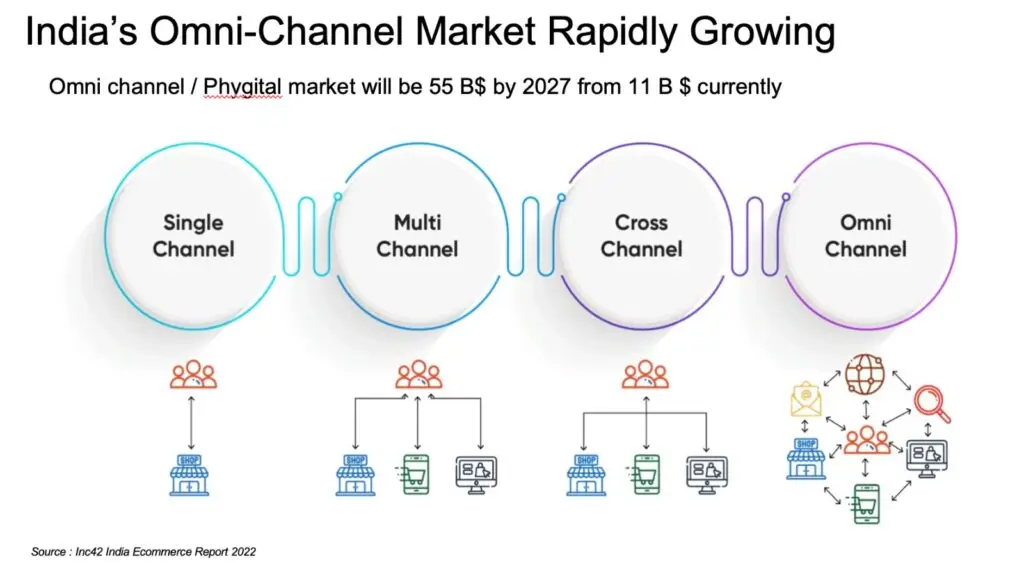
Omni channel refers to a multichannel approach to marketing, sales, and customer service that provides customers with a seamless and integrated shopping or communication experience across various channels and touchpoints. These channels can include physical stores, websites, mobile apps, social media, email, phone, and more.
India’s e-retail market is estimated to scale to $57–$60 billion in 2023, adding $8–$12 billion annually since 2020 . India’s omnichannel surge stems from a long-standing consumer habit of “research online, buy offline” or vice versa.
This trend is forcing digital brands to build brick-and-mortar stores, while traditional FMCGs are entering the online arena for the first time. This shift empowers customers with ultimate shopping flexibility, buying anytime and anywhere. E-commerce accounts for 7-8% of all sales but it is growing and is a part of the overall shopping experience that customers are increasingly adopting as they become enabled by technology. This calls for an integrated physical and digital i.e. “phygital” approach, especially for growing digital first brands.
What is Omni Channel?
In the context of modern commerce, a preliminary understanding and beginning point can be grasped from this definition: “The prefix “omni” means “all,” and “channel” is a reference to the many ways customers might interact with a company—in physical stores, by surfing the web, on social media, and in emails, apps, SMS, and other digital spaces.” (Source: McKinsey & Company)
Omni channel refers to the integration of various sales and marketing channels to create a unified and seamless customer experience. It goes beyond the traditional multi-channel approach by not only providing customers with multiple touchpoints but also ensuring a consistent and personalized experience across all channels.
Read more – How Omnichannel Sales Drive Business Growth?
There are three aspects of Omni Channel every brand has to master :
A. Omni Channel Marketing: Where customers are influenced by TV, Social, Digital marketing.
B. Omni Channel Sales: Where customers can buy online, stores, marketplaces, or on calls.
C. Omni Channel Servicing: Customer can interact with the brand across all channels and served equally.

Omnichannel is a response to changing consumer behavior, which often involves researching products and making purchases through multiple channels. Businesses that successfully implement omnichannel strategies can enhance customer loyalty, increase sales, and improve overall customer satisfaction by providing a convenient and tailored experience across all touchpoints.
Why are companies going omni-channel?
The shift towards omni channel is driven by the desire to meet the evolving needs and expectations of customers. In today’s digital age, customers expect convenience, personalization, and a consistent experience across all channels.
- By adopting an omni channel approach, companies can provide a seamless customer journey, resulting in increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, sales.
- Omnichannel customers tend to spend more than single-channel customers. By providing multiple avenues for customers to engage and make purchases, businesses can capture more sales opportunities.
- Omnichannel strategies generate valuable data that can be used to understand customer behaviour, preferences, and buying patterns. This data can inform marketing efforts and product offerings.
- Moreover, omni channels allow businesses to tap into new markets and reach a wider audience. By leveraging various channels like Google, Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube, businesses can connect with customers at different touchpoints and maximize their visibility.
Channels can be thought of as touchpoints or interfaces, physical and digital, that facilitate a transaction/engagement of any kind between a customer and an organisation/company. The experience that a customer has engaging with your company on those channels determines multiple elements of their likelihood to make a purchase, come back to avail of your service or buy your product, recommend it to friends and family, and whether they will talk about it on social media.
Information sharing in the public realm has become extremely fast and if companies aren’t quick to catch trends they lose out on important moments and time.
Source: Harvard Business Review, Ofek, E., & Wathieu, L. (2010, July-August)
Offline to Online
One way that brick-and-mortar businesses can expand their growth is through adding an online store. This is because of the phenomenal growth of the e retail market. By expanding their brick-and-mortar businesses beyond the geographic limitations of their storefronts, retailers can tap opportunities by reaching new audiences and potential customers.
Examples of brands who expanded from offline to online
- Decathlon, a renowned sports retailer, allows customers to browse and purchase products both online and in-store.
- Offline retail stores like Croma, Reliance Digital and Vijay Sales have forayed into online channels.
- Reliance brands like Jio, Trends also provide customers with a seamless experience across their online platform and offline stores.
Online to Offline
While the D2C model has helped new brands scale rapidly online, expanding into offline channels has become imperative for the next growth stage. Key factors pushing D2C brands towards adoption of offline models include :
- Access and Experience: Offline stores enable customers to touch, feel, and experience products first-hand before purchasing, building more trust and comfort, especially in categories like apparel, cosmetics, and food.
- Mainstream Adoption: Digital-native consumers were early adopters of D2C brands. However, offline retail is critical for appealing to mainstream audiences.
- Cost Efficiencies: Establishing offline distribution networks leads to cost efficiencies compared to pure e-commerce models, which rely heavily on last-mile delivery.
- Market Penetration: Online sales are predominantly concentrated in Tier 1 and 2 cities. Offline retail is crucial for deeper penetration into Tier 3-6 towns and rural markets.
Source: Inc42 report
Examples of brands who expanded from online to offline
- A social proofing of e-retailers goes a long way in embedding a brand in a customer’s mind and explains Lenskart’s foray into offline retail in a strategic and phased manner after launching in 2010 to becoming the largest optical retail chain in India. Also Read – Crafting Winning O2O Strategies for Omnichannel Growth
- Nykaa opened up offline stores to further solidify their presence in the beauty space.
Other brands which have expanded offline include Caratlane, Sugar Cosmetics, GIVA among many others.
Read more – CaratLane’s Omnichannel Journey: Redefining the Future of Jewellery Shopping
These moves are aimed at building awareness and trust, responding to customer preference of trying a product before purchasing, valuable in-store services, and building brand equity.
What is Omni Channel Marketing vs Omni Channel Sales?
With omni-channel selling, customers can use several sales channels to help them make a single purchase, from doing their research and finding what they’re looking for, to eventually placing an order. All of these sales channels must be integrated in order to be classified as an omni-channel strategy (Source: Zoho.com).
Omnichannel marketing is a way for brands to promote their products or services across multiple channels including social media, tv, sms, whatsapp, email leveraging unified messaging, visuals and offers. Omnichannel marketing is the effective guidance of customers to the right product and/or service that they are looking for with the right amount of service. It incorporates the seamless integration of all channels that a customer engages with, carrying forward the customer’s preferences and settings.
“Customers also engage with 3 to 5 channels when they make a purchase or resolve a request.”
Source: McKinsey
Whereas, a market study conducted with respondents across 18 nations asserts that 77% of Indians prefer to shop from a brand that has an omnichannel presence (Source: Economic Times). Younger buyers and Gen-Z especially prefer omnichannel marketing and retail options and look for a hassle-free experience in shopping. This cohort also spends a significant time on social media channels and they engage with companies and brands online, often engaging in conversations with them especially on X (formerly Twitter).
Instagram, Facebook, YouTube and Google Search are platforms that allow brands to not just advertise but also sell seamlessly, either by routing a customer to the brand’s app or website, or through their marketplaces.
Key aspects of omnichannel marketing that make for a truly exceptional service for customers:
- Personalized marketing agenda for each customer with autonomy to opt in or out of channels that they want to receive messaging from
- Enhancing customer experience with relevant messaging and product recommendations
- Create digital touchpoints along with in-store capabilities: mobile apps, digital displays, interactive screens, tech-enabled associates, and point-of-sale
- Creating an ecosystem around your brand that extends beyond product and focuses on innovative offers, content and community interactions
- Leveraging USPs by creating a separate channel for specialized products or service
Zomato went from being a food delivery app to developing an ecosystem around food and cuisine with a focus on marketing across multiple platforms and innovating with content and influencer marketing through blogs and videos, that elevated the brand beyond mere delivery and a personalization through AI-powered restaurant recommendations and deals cemented in customer loyalty.
Measuring the impact of Omni Channel Business
Measuring the impact of an omni channel business requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account various metrics and analytics. Here are some key metrics to consider:
- Sales and Revenue: Tracking the overall sales and revenue generated through different channels can provide insights into the effectiveness of the omni channel strategy.
- Customer Engagement: Monitoring metrics such as website traffic, social media interactions, and email open rates can help gauge customer engagement across channels.
- Customer Satisfaction: Collecting feedback and conducting surveys can help measure customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
- Omni Channel Conversion: As customers get influenced from one channel and they complete the purchase on another, understanding Omni Channel Conversion of online to offline and offline to online is key.
Utilizing tools like Google Analytics can provide in-depth data on customer behaviour, conversion rates, and channel performance.By analyzing these metrics and leveraging advanced analytics, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their omni channel performance and make data-driven decisions to optimize their strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, omni-channel isn’t merely a buzzword; it’s a transformative approach revolutionizing customer-business interactions. Advancements in technology make omni-channel solutions affordable and accessible, even for smaller businesses. Cloud-based platforms and data analytics enable efficient management across multiple channels without hefty investments. Integrating online and offline experiences, utilizing digital marketing channels, and measuring impact through analytics fosters a customer-centric strategy driving growth and success.
The future of businesses is neither pure online or pure offline, businesses to grow and survive will have to be Omni Channel in true sense. 🛒
Effective strategies to drive omnichannel growth are:
- Use of First Party data to drive Marketing effectiveness. (Link to the blog)
- Effective use of WhatsApp Marketing (Link to the blog)
- Effectively leveraging omnichannel transmission technologies such as QR codes (Link to the blog)
At DAIOM we offer consulting services around driving marketing efficiency and omnichannel growth . To know more about how your brand can build effective omni channel strategies, write to us at saurabh@daiom.in
Subscribe to our Newsletter to get the access to the blog!


