Acquiring new customers today is not just challenging—it’s costly. Over the past five years, the cost of customer acquisition has increased by more than 50%, making it more expensive than ever to attract new customers.
Yet, despite this rising cost, many businesses continue to prioritize finding new customers over nurturing existing ones. However, retaining customers is often far more valuable.
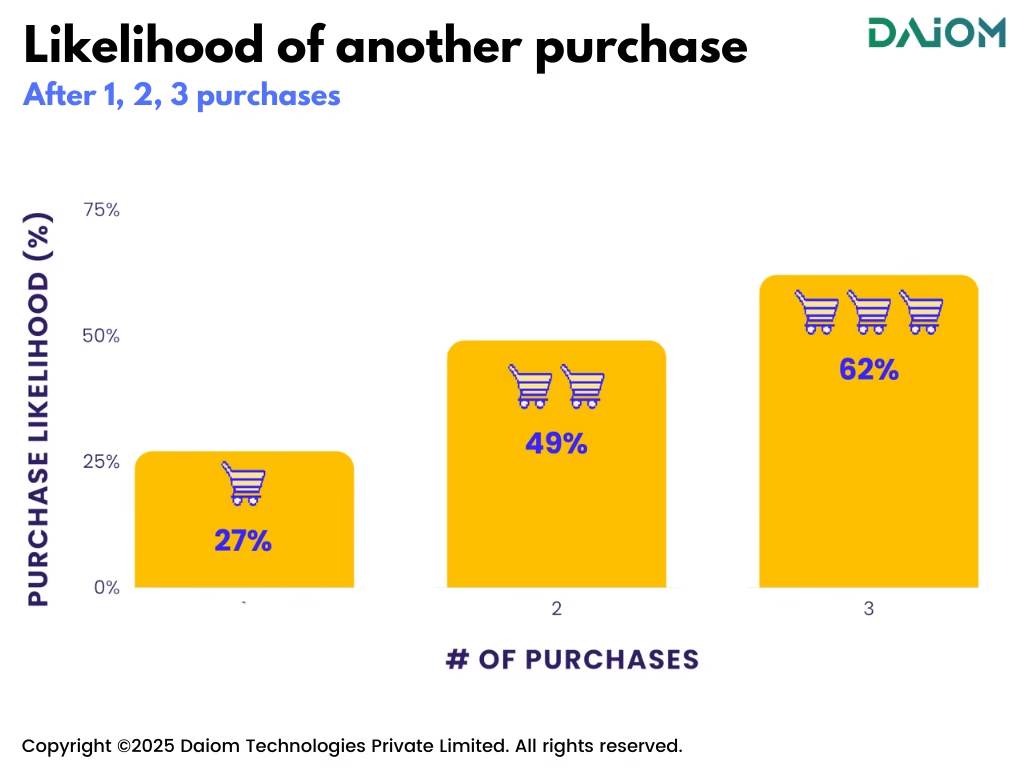
Studies show that repeat customers are significantly more likely to buy again compared to first-time buyers. They already trust your brand, are familiar with your products, and require less convincing—making them a crucial driver of long-term business growth.
Moreover, the chance of selling to a repeat customer is 60%-70%, while for a new customer, it’s only 5%-20%. Plus, repeat customers spend more, refer friends, and help your business grow over time.
So, how do you track and improve customer loyalty?
That’s where Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) comes in.
This metric tells you how many of your customers return for another purchase. A higher RCR means stronger loyalty, lower marketing costs, and more revenue.
In this blog, we’ll explain what Repeat Customer Rate is, how to calculate it, and simple ways to boost it—so you can grow your business without always chasing new customers.
If you can get 20-30% of customers coming back every month and making a purchase from your store, you should do pretty well.
Alex Schultz, VP of Growth at Facebook
Table of Contents
1. How to Identify a Repeat Customer?
A repeat customer is someone who has made more than one purchase from a website, app or store. These customers are valuable because they are more likely to buy again and contribute to long-term growth.
To track repeat customers, brands can use tools like:
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) – Most eCommerce platforms have reports that show how many buyers are new vs. returning.
- Google Analytics – Go to Audience Insights > Behavior > New vs. Returning Users to see how many repeat buyers you have and how much revenue they generate.
By monitoring these insights, brands can focus on retention strategies to turn more first-time buyers into loyal customers.
3.1 Why Do You Need to Calculate Repeat Customer Rate?
Repeat customers are the backbone of a profitable business. They don’t just buy again—they help your business grow in multiple ways. Here’s why tracking Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) is essential:
- Higher Revenue & Profitability: Repeat customers tend to spend more per purchase and have a higher lifetime value than new buyers. This directly boosts your business’s profitability without needing constant new customer acquisitions.
- Lower Marketing Costs: It’s expensive to bring in new customers. By increasing your repeat customer base, you can reduce marketing costs and get more value from those who already know and trust your brand.
- Valuable Customer Insights: Loyal customers often provide honest feedback, helping you refine your products and services. Their insights can lead to better offerings and improved customer experience.
- Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Satisfied repeat customers are your best brand ambassadors. They are more likely to refer friends and family, helping you attract new customers organically.
3.2 What is Repeat Customer Rate (RCR)?
Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) is a key metric that tracks how often customers return to make additional purchases. It helps businesses understand customer loyalty and ongoing engagement.
Read More – Points Vs. Cashback: What Drives Customer Loyalty?
A high RCR means customers are consistently coming back, increasing their Lifetime Value (LTV) and strengthening long-term revenue. This is crucial because repeat rate directly impacts LTV, showing how much value a customer provides over their entire relationship with a brand.
Read more – Metric of the Week: Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
On the other hand, a low RCR suggests that a business may be relying too much on new customers, highlighting potential gaps in customer retention strategies.
But RCR isn’t just about whether a customer makes a second purchase—it reflects the overall customer experience across multiple transactions. A strong RCR indicates that customers find value in your brand, while a weak one signals the need for better engagement and retention efforts.
How to Calculate Repeat Customer Rate (RCR)?
Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) helps businesses understand how many customers return for additional purchases. It’s a simple yet powerful metric to measure customer loyalty and retention.
Formula for RCR:
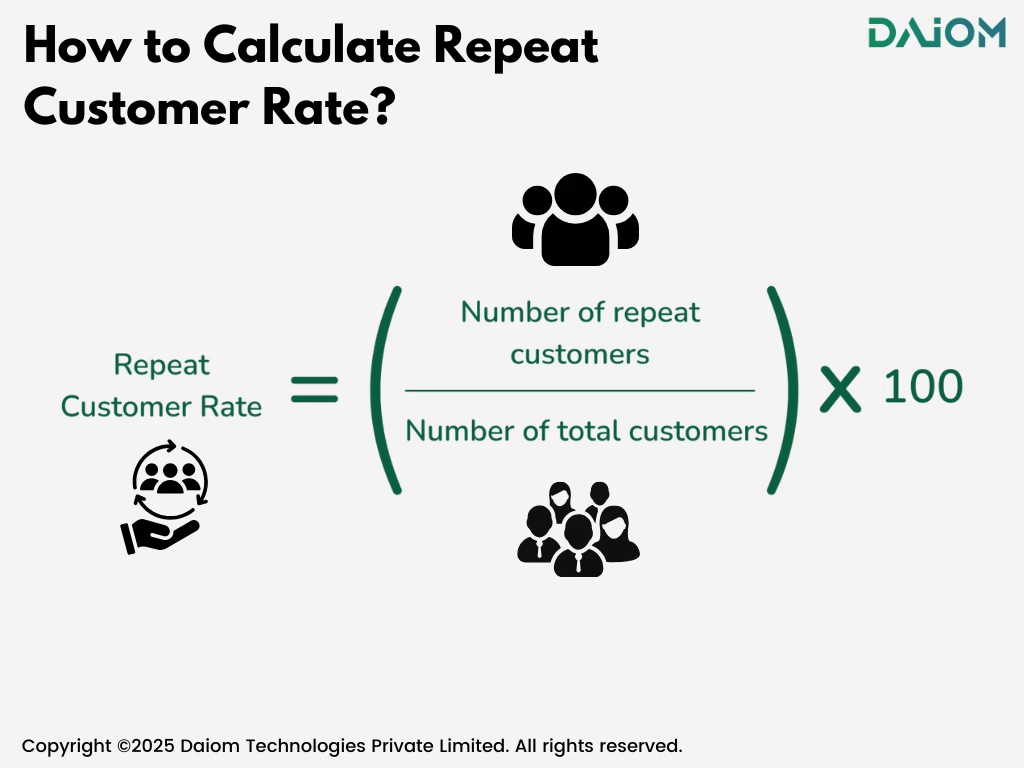
Repeat Customer Rate = (Total Repeat Customers ÷ Total Paying Customers) × 100
Example Calculation:
For example, a fashion eCommerce brand wants to track its customer loyalty.
- In February 2025, the brand had 1,500 total customers who placed an order.
- Out of these, 750 customers made another purchase within the same month.
The Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) would be:
(750 ÷ 1,500) × 100 = 50%
This means 50% of customers returned to buy again, indicating strong customer loyalty driven by good product quality, engagement strategies, or post-purchase experience.
3.3 Importance of Time Frame in Repeat Rate
Measuring Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) without considering the timeframe can be misleading. Different industries have unique purchase cycles, and analyzing RCR without aligning it to these cycles can lead to incorrect conclusions.
For example, a high repeat rate within a month might be expected for a grocery delivery app but unrealistic for a luxury watch brand. To get accurate insights, businesses should measure RCR over different periods:
- 1-month RCR → Best for fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) like groceries and daily essentials where frequent purchases are expected.
- 3-month RCR → Ideal for fashion, skincare, and consumer electronics, where customers tend to make repeat purchases within a quarter.
- 6-month RCR & beyond → Relevant for industries like furniture, automobiles, and luxury goods, where customers purchase infrequently but at higher order values.
Aligning RCR measurement with the appropriate timeframe ensures accurate benchmarking and strategic decision-making.
3.4 Industry-Specific Differences in Repeat Rates
Repeat customer rates vary drastically across industries. Comparing RCR across different sectors doesn’t provide useful benchmarks. Instead, businesses should analyze RCR within their industry:
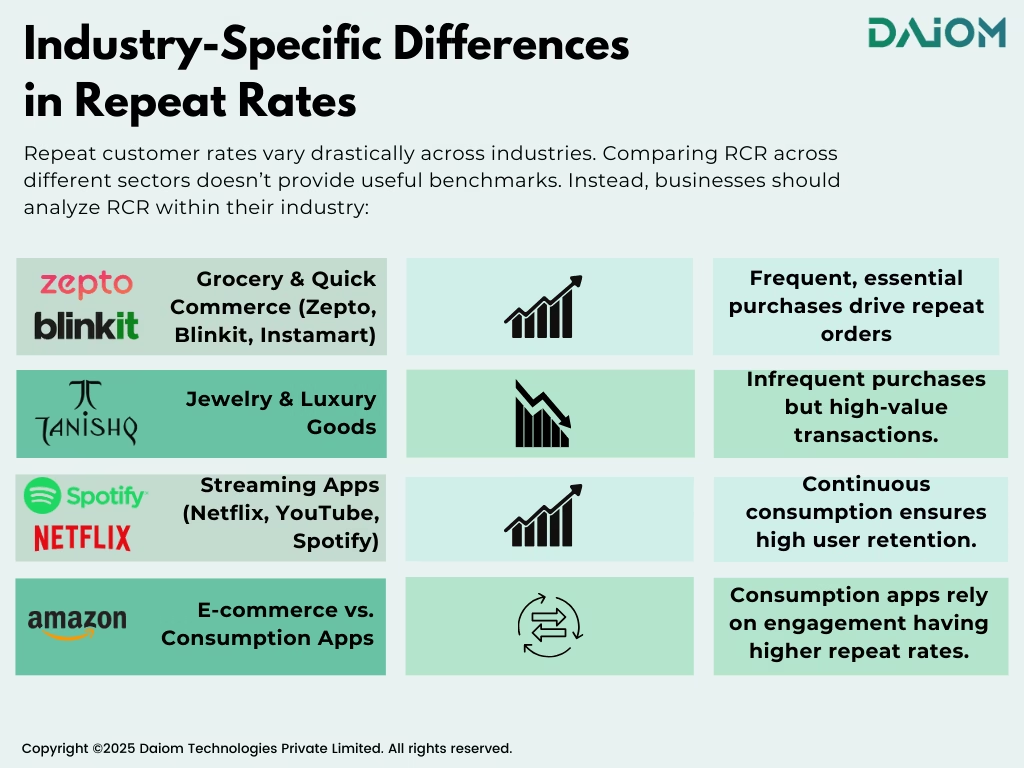
- Grocery & Quick Commerce (Zepto, Blinkit, Instamart): High RCR due to frequent, essential purchases.
- Jewelry & Luxury Goods: Lower RCR since purchases are less frequent but involve high-value transactions.
- Streaming & Content Apps (Netflix, YouTube, Spotify): Extremely high RCR as they rely on continuous consumption rather than discrete transactions.
- E-commerce vs. Consumption Apps: Platforms like YouTube and Netflix don’t rely on transactions but rather on user engagement, making their repeat rates significantly higher than traditional commerce businesses.
Businesses should use industry-specific benchmarks to evaluate their RCR realistically and set achievable retention goals.
3.5 Repeat Rate with a Cohort View
Tracking Repeat Rate in cohorts provides deeper insights into customer retention trends. Instead of looking at an overall repeat rate, businesses should analyze RCR based on customer acquisition cohorts.
- Example: If a brand acquires 1,000 customers in January and 300 of them make a second purchase by March, the 3-month repeat rate for the January cohort is 30%.
- Cohort-based analysis helps businesses understand:
- How different customer segments behave over time.
- Whether first-time buyers are turning into loyal customers.
- The impact of specific marketing campaigns on repeat purchases.
By analyzing RCR at a cohort level, brands can refine their customer retention strategies and optimize engagement based on actual buying patterns.

3.6 What Brings a Good Repeat Rate?
A strong repeat customer rate doesn’t happen by chance. Businesses that excel at customer retention focus on key factors such as:
- Exceptional Customer Experience: High-quality service, seamless checkout, fast delivery, and proactive support encourage customers to return.
- Understanding Customer Behavior: Segmenting customers based on preferences and behaviors helps in tailoring offers that drive repeat purchases.
- Personalized Engagement: Targeted recommendations, customized incentives, and loyalty rewards enhance customer retention.
3.7 How to Avoid the Common Mistakes?
Many businesses struggle with increasing their Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) because they fall into common pitfalls. Simply measuring repeat purchases isn’t enough—brands must ensure they are engaging customers effectively and optimizing their retention strategies. Here are three key mistakes to avoid:
One-Size-Fits-All Approach: Not all customers are the same, so using generic messaging for all buyers can lead to disengagement. Customers expect personalized experiences that cater to their interests, past behavior, and preferences.
What to Do Instead:
- Segment your audience based on purchase history, frequency, and preferences.
- Personalize email campaigns, push notifications, and in-app messages with tailored product recommendations.
- Offer exclusive deals or incentives based on what the customer has previously purchased.
For example, a beauty brand can send personalized recommendations for skincare products based on a customer’s previous purchases instead of sending the same promotional email to everyone.
Mass Promotions: Brands often rely on blanket discounts to increase repeat purchases, but this can dilute brand value and attract price-sensitive customers rather than loyal buyers. Overusing discounts also reduces profit margins and trains customers to only shop during sales.
What to Do Instead:
- Focus on loyalty-based rewards rather than mass discounts.
- Offer exclusive benefits like early access to new products, free shipping, or members-only perks to encourage repeat purchases.
- Implement targeted discounts based on individual customer behavior instead of sitewide sales.
For example, an electronics brand can offer a special discount on accessories for customers who recently purchased a laptop, rather than running a storewide sale.
Ignoring Engagement Metrics: Repeat rate is not just about transactions. If a customer isn’t purchasing but is still engaging with your brand (e.g., browsing products, adding items to a wishlist, or interacting with emails), they are still interested. Many businesses fail to track these engagement signals and miss opportunities to nurture repeat purchases.
What to Do Instead:
- Track non-transactional behaviors such as product page views, app logins, email opens, and cart activity.
- Set up automated engagement campaigns to re-engage customers who show interest but haven’t purchased yet.
- Use AI-driven recommendations to remind customers about items they previously viewed or added to their cart.
For example, a fashion retailer can send a gentle reminder if a customer added a product to their cart but didn’t check out, nudging them toward completing the purchase.
3.8 Buying vs. Consumption: RCR Beyond Orders
Repeat rate isn’t just about placing another order. In some industries, repeat engagement is just as valuable as repeat purchases:
- Netflix measures how often users stream content.
- Retailers track store visits and online browsing habits.
- Food delivery apps analyze app open rates and engagement, not just orders placed.
Businesses should define repeat behavior based on their industry’s key engagement metric to get a holistic view of customer retention.
4. How to Improve Repeat Purchase Rate?
Boosting RCR requires a data-driven, strategic approach. Here’s how businesses can improve their repeat purchase rate:
- Identify the Ideal Time Window: Analyze customer data to determine when first-time buyers are likely to make a second purchase and target them accordingly.
- Segment Customers Based on Buying Patterns: Group customers into cohorts based on purchase frequency and tailor marketing messages to each group.
- Engage with Targeted Nudges: Use personalized recommendations, reminders, and push notifications to encourage repeat purchases.
- Offer Valuable Incentives:
- Personalized Discounts: Offers based on past purchases increase the likelihood of another buy.
- Loyalty Programs: Encourage long-term commitment by rewarding frequent buyers.
- Exclusive Perks: VIP access, early sales, and premium content boost customer retention.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can create a strong retention framework, ensuring long-term customer loyalty and sustained revenue growth.
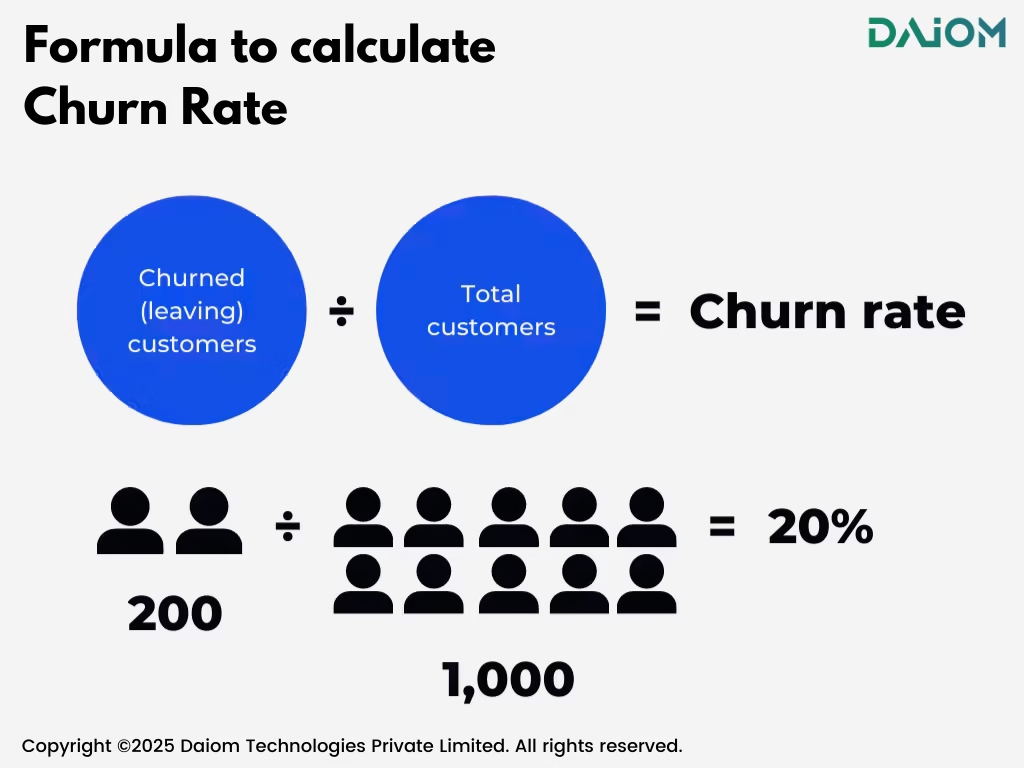
4.1 Repeat Rate vs. Churn Rate
While Repeat Rate measures customer retention, Churn Rate tracks the percentage of customers who stop purchasing. Understanding both metrics together helps businesses identify gaps in customer retention.
- High RCR + Low Churn Rate → A strong customer base that keeps coming back, indicating successful retention strategies.
- Low RCR + High Churn Rate → A warning sign that customers aren’t returning after their first purchase, requiring improvements in post-purchase engagement.
- High RCR + High Churn Rate → Customers may repurchase but also leave quickly, possibly due to price sensitivity or competitors offering better deals.
To reduce churn and improve repeat purchase rates, businesses must focus on:
- Personalized follow-ups → Engaging first-time buyers with tailored recommendations.
- Loyalty incentives → Encouraging repeat purchases with rewards and exclusive offers.
- Customer experience enhancements → Improving service, delivery speed, and overall satisfaction.
Acquiring a new customer is anywhere from five to 25 times more expensive than retaining an existing one.
Harvard Business Review
5. Conclusion
Repeat Customer Rate (RCR) isn’t just a number, it’s a key indicator of business success. A strong RCR means lower acquisition costs, higher profits, and loyal customers who keep coming back.
By focusing on retention strategies like loyalty programs, personalized offers, and excellent post-purchase experiences, businesses can boost their repeat purchase rate and drive sustainable growth.
Instead of constantly chasing new customers, invest in the ones you already have. Improve their experience, reward their loyalty, and watch your business thrive!
If you’d like to discuss how we can help enhance your customer repeat rate and optimize your strategies, we’d be happy to set up a consultation call. Feel free to reach out to us at alibha@daiom.in
For more informative content and blog, follow and stay tuned to DAiOM.
Subscribe to our NEWSLETTER!


